Table Of Content
The results of this research component, called the “sense” (“Lesart”), are subsequently compared to the results of the other component, called the “anti-sense” (“alternative Lesart”), which are considered dissonant, unexpected, and/or contrary to what had been found in the literature. The aim is to develop an overall explanation that fits both the sense and the anti-sense (Bazeley and Kemp 2012; Mendlinger and Cwikel 2008). Finally, a reanalysis of the data can sometimes lead to resolving divergence (Creswell and Plano Clark 2011). Dependent research activities include a redirection of subsequent research inquiry.
Purpose
Of course, the drawback of the Pocock strategy is that if the study cannot be terminated after the first stage, it then only has about 2% of alpha left for the final stage. Inspecting the probabilities stage by stage, 2.93% of alpha is spent at the first and 2.04% at the second stage, respectively. That is, although the nominal bounds are identical at both stages, due to the asymmetric shape of the two-dimensional distribution, the resulting probabilities are different.
5. Results from the Statistical Analysis
This researcher takes as his or her starting point the logic and philosophy of mixed methods research. These mixed methods researchers are likely to believe that qualitative and quantitative data and approaches will add insights as one considers most, if not all, research questions. For validity, an instrument must be able to accurately compute the value it is meant to ascertain [43]. The internal consistency of collected data is also critical for its validity [22]. Furthermore, the collected data must fulfil the minimum requirements defined by the sampling method in terms of quantity and form [44]; this is particularly useful in dealing with erroneous or missing data.
5. Survey Data Collection Procedure
Something similar applies to the classification of the purposes of mixed methods research. The classifications of purposes mentioned in the “Purpose”-section, again, are basically meant for the classification of whole mixed methods studies. In practice, however, one single study often serves more than one purpose (Schoonenboom et al. 2017). The more purposes that are included in one study, the more difficult it becomes to select a design on the basis of the purpose of the investigation, as advised by Greene (2007). Of all purposes involved, then, which one should be the primary basis for the design?
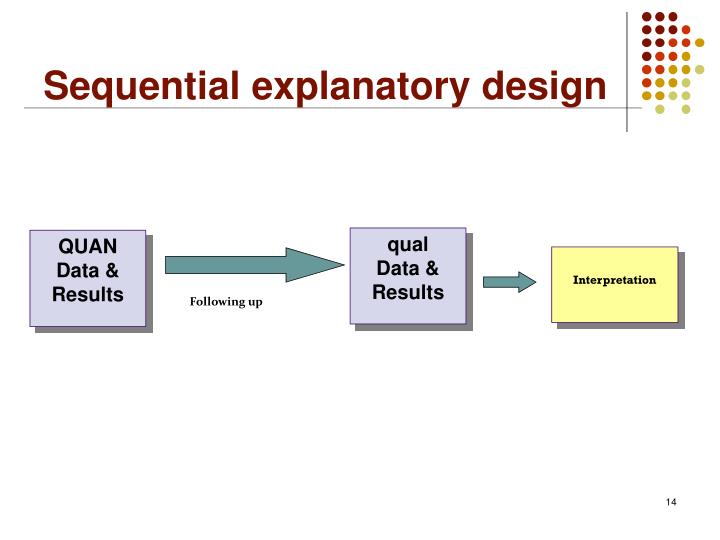
In the case of development, integration consists of an adjustment of an, often quantitative, for example, instrument or model or interpretation, based on qualitative assessments by members of the target group. Simultaneity (“Simultanität”) forms the basis of the distinction between concurrent and sequential designs. In a sequential design, the quantitative component precedes the qualitative component, or vice versa. In the notation of Morse (1991), concurrence is indicated by a “+” between components (e. g., QUAL + quan), while sequentiality is indicated with a “→” (QUAL → quan). Note that the use of capital letters for one component and lower case letters for another component in the same design suggest that one component is primary and the other is secondary or supplemental.
Longitudinal design is when data is collected from the same group of participants repeatedly over different points in time. This is another way to examine the effects that a treatment or variable might have on subjects. In this design, researchers observe a single group on at least two different occasions. The first observation occurs before the group receives special treatment as a way to establish a baseline for how subjects behave in the absence of the variable of interest.
Future Developments or Limitations
Multiregional clinical trials have been accepted in recent years as a useful means of accelerating the development of new drugs and abridging their approval time. The statistical properties of multiregional clinical trials are being widely discussed. In practice, variance of a continuous response may be different from region to region, but it leads to the assessment of the efficacy response falling into a Behrens–Fisher problem—there is no exact testing or interval estimator for mean difference with unequal variances.
Group Sequential Designs: A Tutorial
One Design, Two Products: The SanDisk Ultra 3D (1TB) and WD Blue 3D (1TB) SSD Reviews, with BiCS 3D NAND - AnandTech
One Design, Two Products: The SanDisk Ultra 3D (1TB) and WD Blue 3D (1TB) SSD Reviews, with BiCS 3D NAND.
Posted: Thu, 14 Sep 2017 07:00:00 GMT [source]
We leave it to the reader to decide if he or she desires to conduct a qualitatively driven study, a quantitatively driven study, or an equal-status/“interactive” study. According to the philosophies of pragmatism (Johnson and Onwuegbuzie 2004) and dialectical pluralism (Johnson 2017), interactive mixed methods research is very much a possibility. By successfully conducting an equal-status study, the pragmatist researcher shows that paradigms can be mixed or combined, and that the incompatibility thesis does not always apply to research practice. Equal status research is most easily conducted when a research team is composed of qualitative, quantitative, and mixed researchers, interacts continually, and conducts a study to address one superordinate goal.
Sequential Trigon-6 is the final analogue synth created by the late Dave Smith - MusicTech
Sequential Trigon-6 is the final analogue synth created by the late Dave Smith.
Posted: Thu, 17 Nov 2022 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Cross-Sequential Research
Since only one cohort is being studied, there is no way to know if findings would be different from other cohorts. In addition, changes that are found as individuals age over time could be due to age or to time of measurement effects. That is, the participants are tested at different periods in history, so the variables of age and time of measurement could be confounded (mixed up). For example, what if there is a major shift in workplace training and education between 2020 and 2040 and many of the participants experience a lot more formal education in adulthood, which positively impacts their intelligence scores in 2040? Researchers wouldn’t know if the intelligence scores increased due to growing older or due to a more educated workforce over time between measurements.
An investigation, in Morse and Niehaus’s (2009) view, is focused primarily on either exploration-and-description or on testing-and-prediction. In the first case, the theoretical drive is called “inductive” or “qualitative”; in the second case, it is called “deductive” or “quantitative”. In the case of mixed methods, the component that corresponds to the theoretical drive is referred to as the “core” component (“Kernkomponente”), and the other component is called the “supplemental” component (“ergänzende Komponente”).
It is conceivable that one simultaneously conducts interviews and collects questionnaire data (concurrent), while allowing the analysis focus of the interviews to depend on what emerges from the survey data (dependence). In the mixed methods literature, the distinction between sequential and concurrent usually refers to the combination of concurrent/independent and sequential/dependent, and to the combination of data collection and data analysis. For example, in a conversion design, qualitative categories and themes might be first obtained by collection and analysis of qualitative data, and then subsequently quantitized (Teddlie and Tashakkori 2009). Likewise, with Greene et al.’s (1989) initiation purpose, the initiation strand follows the unexpected results that it is supposed to explain. G., to collect interview data and survey data of one inquiry simultaneously; in that case, the research activities would be concurrent.
On the other hand, if I say that more people will watch this lesson if it was read in a British accent, then that would be said to have high ecological validity. The figure below shows how the time point of the stage 1 analysis affects the correlation of the stages and with that shapes the design probabilities. Bivariate normal density with critical bounds of Pocock (left) and O’Brien-Fleming design (right) both with interim analysis after 50% of the sample. In contrast, the Pocock design appears to be more “aggressive” trying harder to terminate the study early.
The tool used for the structural analysis is the Matrix of Cross Impacts-Multiplication Applied to a Classification (MICMAC) method, defined according to Leśniak and Górka [50], as a method that “consists of raising the structural analysis matrix to a power of successive values. In this way, thousands and millions of lines are analysed in most concrete systems” (p. 13). Each of these has distinct advantages and disadvantages, including cost, time, and subjects.

No comments:
Post a Comment